Monte Carlo Simulation
Assess and manage project uncertainty and risk, enabling better decision-making and improving project outcomes.
Moises Romero
What Is Monte Carlo Simulation?
A Monte Carlo simulation is a technique used to assess the impact of uncertainty and risk on project schedules, costs, or other key metrics. It involves running multiple simulations using random values for uncertain variables within specified ranges to model different possible outcomes for the project.
It typically works:
- Identify uncertain variables: These could include factors such as task durations, resource availability, external dependencies, or market conditions that could affect the project.
- Define probability distributions: Assign probability distributions to each uncertain variable. For example, task durations might follow a triangular distribution based on optimistic, most likely, and pessimistic estimates.
- Run simulations: Using Monte Carlo simulation software or tools (Microsoft Excel, Palisade @RISK, Oracle Crystal Ball, Simul8, AnyLogic, Python, R), the project model is simulated numerous times (often thousands or more) with different random values drawn from the defined probability distributions for each uncertain variable.
- Analyze results: The simulation generates a range of possible outcomes for the project, including potential completion dates, costs, or other metrics. Through statistical analysis of the simulation results, you can identify the likelihood of meeting project deadlines, staying within budget, or achieving other project objectives.
- Risk mitigation: Based on the simulation results, teams can identify high-risk areas and develop strategies to mitigate those risks. This might involve adjusting project plans, allocating additional resources, or implementing contingency plans.
Why Do Monte Carlo Simulation?
Monte Carlo simulation is a valuable practice for several reasons:
- Accounting for uncertainty: Projects are inherently uncertain, with various factors such as task durations, resource availability, and external dependencies subject to change. Monte Carlo simulation allows project managers to incorporate this uncertainty into their planning and decision-making process, leading to more realistic project schedules, budgets, and risk assessments.
- Quantifying risk: By running multiple simulations with different sets of random values for uncertain variables, Monte Carlo simulation provides a range of possible outcomes for the project. This allows teams to quantify the likelihood of meeting project deadlines, staying within budget, or achieving other project objectives, helping them better understand and manage project risk.
- Identifying critical areas: Monte Carlo simulation highlights areas of the project that are most sensitive to uncertainty and risk. By analyzing the simulation results, teams can identify high-risk tasks, resources, or dependencies that may need closer attention or additional mitigation strategies.
- Optimizing resource allocation: Understanding the range of possible project outcomes enables teams to optimize resource allocation and contingency planning. They can allocate resources more effectively to critical tasks or areas of the project with higher uncertainty, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and effectively.
- Enhancing decision-making: Monte Carlo simulation provides teams with valuable insights into the potential impacts of different decisions and strategies on project outcomes. Armed with this information, teams can make more informed decisions, prioritize actions, and communicate project risks and uncertainties more effectively to stakeholders.
How to do Monte Carlo Simulation?
Step 1: Identify Uncertain Variables
Identify the key uncertain variables in your project. These could include:
- Task durations
- Resource availability
- External dependencies
- Market conditions
- Any other factors that could impact project outcomes.
Step 2: Define Probability Distributions
For each uncertain variable, define the probability distribution that represents its uncertainty. Common distributions include:
- Triangular distribution: Useful for representing variables with three-point estimates (optimistic, most likely, pessimistic).
- Normal (Gaussian) distribution: Appropriate for variables where the data follows a bell-shaped curve.
- Uniform distribution: Suitable for variables with equal likelihood across a range of values.
For example, task durations might be represented using a triangular distribution based on optimistic, most likely, and pessimistic estimates.
Step 3: Set Up the Simulation
Use Monte Carlo simulation software or tools (Microsoft Excel, Palisade @RISK, Oracle Crystal Ball, Simul8, AnyLogic, Python, R), to set up the simulation model. Input the uncertain variables along with their defined probability distributions.
Step 4: Define Simulation Parameters
Define the parameters for the simulation, including:
- Number of iterations: Determine the number of simulations to run. A larger number of iterations will result in more accurate and reliable results but will require more computational resources.
- Confidence level: Specify the confidence level for the simulation results, typically set at 90% or 95%.
Step 5: Run the Simulation
Execute the Monte Carlo simulation using the defined parameters. The software will randomly sample values from the probability distributions for each uncertain variable and calculate the resulting project outcomes for each iteration.
Step 6: Analyze Results
Once the simulation is complete, analyze the results to understand the range of possible project outcomes. Key analysis tasks include:
- Calculating summary statistics: Compute mean values, standard deviations, percentiles, and other relevant metrics for project performance indicators such as duration, cost, and resource utilization.
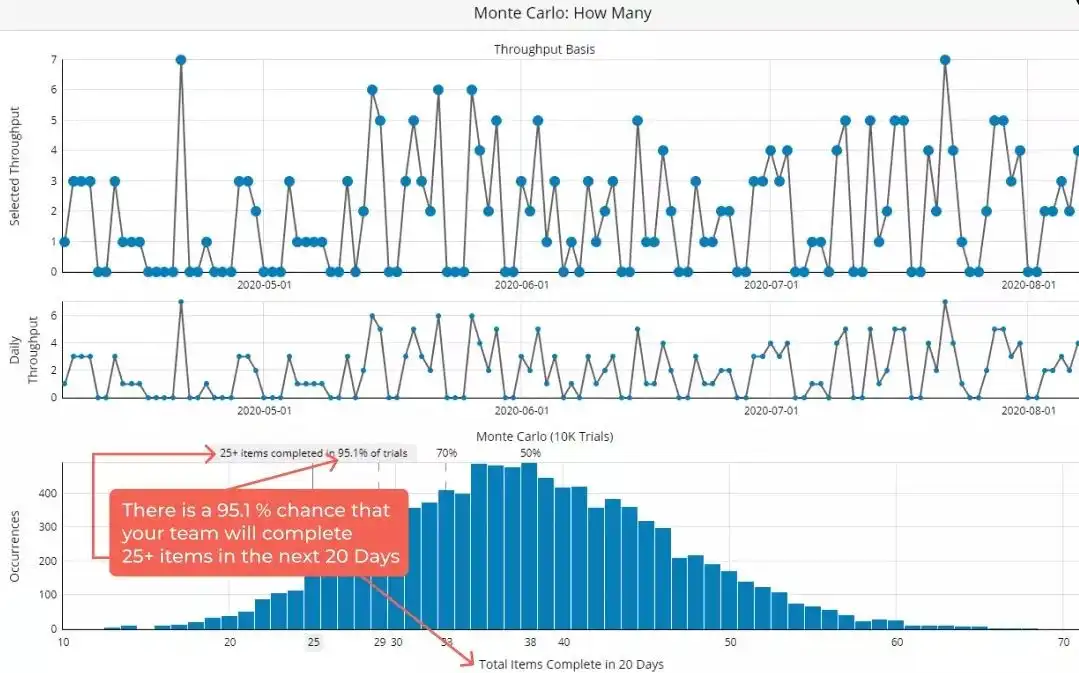
- Creating visualizations: Use charts, graphs, histograms, and probability distributions to visualize the simulation results and gain insights into the variability and uncertainty of project outcomes.
Step 7: Identify Risks and Opportunities
Based on the simulation results, identify areas of the project that are most sensitive to uncertainty and risk. Assess the potential impact of these risks on project objectives and identify opportunities to mitigate or exploit them.
Step 8: Optimize Project Plans
Use the insights gained from the simulation analysis to optimize project plans and resource allocation. Adjust project schedules, budgets, or contingency plans as needed to account for uncertainty and mitigate identified risks. Consider alternative strategies or scenarios to improve project outcomes.
Step 9: Communicate Results
Communicate the findings of the Monte Carlo simulation to project stakeholders. Clearly communicate the level of uncertainty and risk associated with the project and the implications for project planning and decision-making. Use visualizations such as charts, graphs, or probability distributions to effectively communicate complex information.